Epigenetics and Modified Bases
We are interested in understanding chemical modifications to DNA and the effect of such changes to the structure and function of DNA. DNA is made up of four bases – cytosine, guanine, adenine and thymine. However, these bases can naturally undergo chemical modification leading to new bases. Changing one of the bases in a strand of DNA in this way alters its property and function by controlling how the sequence is interpreted. This can affect how genes are switched on and off in different cell types, tissues and organs.
The modified base 5-methylcytosine (5mC) is well-known epigenetic mark that can regulate transcription of the genome. Since 2009 three further modified bases have been detected in the mammalian genome. These are the TET-enzyme generated bases; 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), 5-formylcytosine (5fC) and 5-carboxylcytosine (5caC). The presence of these modifications opens up questions as to their function in normal cellular biology and disease states.
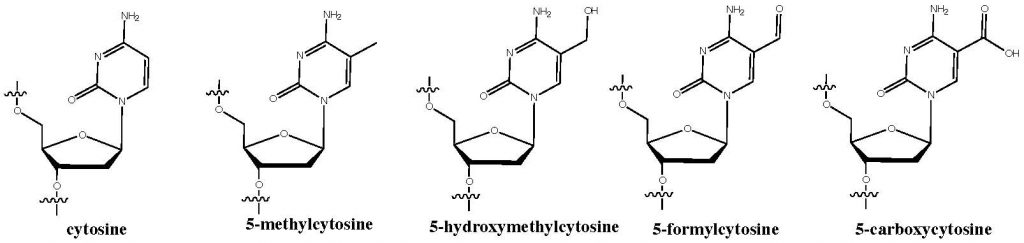
We are developing chemical tools and genomic methods to map and elucidate the function of these modified bases. We are also exploring the molecular basis for their involvement in biological mechanisms. Part of this work exploits state of the art genomics technologies. We have already created methods to quantitatively sequence 5mC, 5hmC and 5fC at single-base resolution. Such tools allow much more accurate study of these epigenetic marks.
The scope of our work will also include the identification, mapping and elucidation of the biological function of other base modifications in the DNA and RNA of various organisms.
References
Sequencing DNA methylation and hydroxymethylation at co-occurring chromatin features
R de Cesaris Araujo Tavares, S Dhir, X He, J Monahan, M Taipale, P Golder, A Ciau-Uitz, W Gosal, D Tannahill and S Balasubramanian
Nature Communications, 2026, in press
DOI:10.1038/s41467-026-69429-6
5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine are synergistic biomarkers for early detection of colorectal cancer
F Puddu, A Johansson, A Modat, J Scotcher, R Sethi, S Yu, N Harding, M Hill, E Lleshi, C Lumby, J Tayssandier, M Wilson, R Crawford, T Charlesworth, P Creed, S Balasubramanian and R J Osborne
Communications Medicine, 2026, 6:12
DOI:10.1038/s43856-025-01278-8
Commentary on ‘Untargeted CUT&Tag reads are enriched at accessible chromatin and restrict identification of potential G4-forming sequences in G4-targeted CUT&Tag experiments’
L Melidis, R de Cesaris Araujo Tavares, X He, S Dhir, D Tannahill and S Balasubramanian
Nucleic Acids Research, 2025, 53:22
DOI:10.1093/nar/gkaf1337
An unnatural base pair for the detection of epigenetic cytosine modifications in DNA
D Schmidl, S M Becker, J M Edgerton and S Balasubramanian
Nat. Chem., 2025, 17, 1732–1741
DOI: 10.1038/s41557-025-01925-6
SCoTCH-seq reveals that 5-hydroxymethylcytosine encodes regulatory information across DNA strands
J S Hardwick, S Dhir, A Kirchner, A Simeone, S M Flynn, J M Edgerton, R de Cesaris Araujo Tavares, I Esain-Garcia, D Tannahill, P Golder, J M Monahan, W S Gosal and S Balasubramanian
PNAS, 2025, 122 (31), e2512204122
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2512204122
DNA G-quadruplex structures act as functional elements in ⍺- and ß-globin enhancers
C Doyle, K Herka, S M Flynn, L Melidis, S Dhir, S Schoenfelder, D Tannahill and S Balasubramanian
Genome Biology, 2025, 26:155
DOI: 10.1186/s13059-025-03627-1